Archives
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-11
- 2018-10
- 2018-07
-
After infection with Salmonella those bacteria that are not
2024-03-11
After infection with Salmonella those bacteria that are not targeted by autophagy of the complete Salmonella-containing phagosome (see above) but are living freely in the cytosol can be eliminated by xenophagy, that is direct targeting of the ‘naked’ bacteria to the autophagic pathway. The type III
-
IGF is an anabolic growth factor that induces hypertrophy an
2024-03-11
IGF1 is an anabolic growth factor that induces hypertrophy and blocks atrophy in skeletal muscle by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway (Egerman and Glass, 2014). In addition to its anabolic and anti-catabolic effects, IGF1 stimulates fatty Retapamulin (FA) uptake and glucose metabolism (Clemmons,
-
Nocodazole mg br Mechanisms of homeostasis At face value hom
2024-03-11
Mechanisms of homeostasis At face value, homeostatic mechanisms may seem like nothing more than a simple balance between opposing forces; however, the ability of Mec1/Tel1 to each orchestrate both negative and positive regulation greatly complicates the system under consideration and argues again
-
Placental cells also express P aromatase
2024-03-11
Placental cells also express P450 aromatase (CYP19A1, encoded by CYP19A1). In the placenta, this enzyme requires an external source of androgens, provided by the adrenal gland of the fetus, to form estrogen. The fetal adrenal gland produces dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) [9] and, in the placenta, it
-
Introduction Preeclampsia a serious hypertensive disorder th
2024-03-11
Introduction Preeclampsia, a serious hypertensive disorder that can occur during pregnancy, is a pregnancy-related disease characterized by the onset of L-690,330 receptor and proteinuria after the 20 t h week of gestation, and it occurs in about 5% of all pregnancies [1]. If left untreated, preecl
-
It was also shown that of crizotinib resistance mechanisms
2024-03-08
It was also shown that 15% of crizotinib resistance mechanisms can be due to an amplification of ALK gene while 30% are caused by a variety of secondary mutations (S1206Y, G1202R, L1196M, C1156Y, G1269A, L1152R, F1174L and 1151Tins) in ALK tyrosine kinase. These mutations can modify the conformation
-
Pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide PACAP is
2024-03-08
Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) is a member of the secretin/growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)/vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) family, with potent anti-inflammatory and potent cytoprotective properties [[6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13]]. PACAP exists as
-
br Functional consequences of ADK regulation on astrocyte
2024-03-08
Functional consequences of ADK regulation on astrocyte function As outlined above (see introduction), ADK critically regulates the extracellular adenosine levels in PPACK Dihydrochloride (Boison, 2006, Etherington et al., 2009). Changes in the levels of adenosine, as a result of the regulation o
-
Molecular docking simulations were carried out for ligands i
2024-03-08
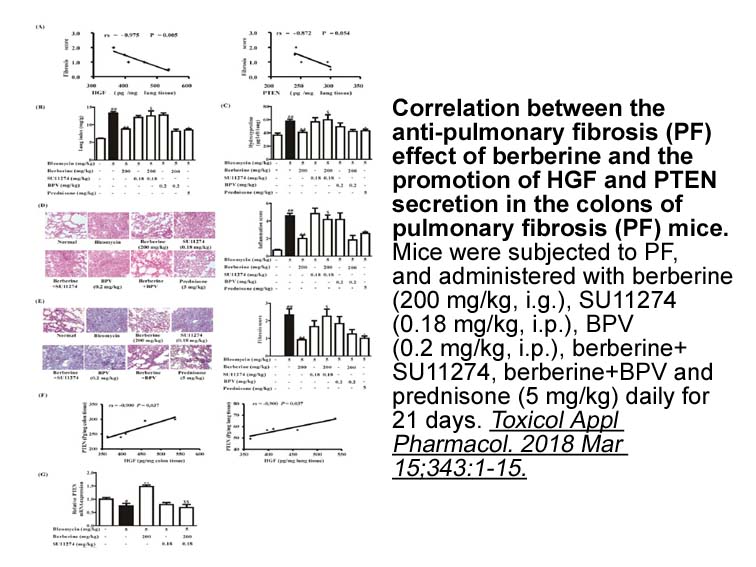
Molecular docking simulations were carried out for ligands – in the ACE crystal structure (1O86) and DPP4 crystal structure (2G5P). Comparison of the binding mode of – () with enalaprilat (a) in ACE shows that the phenethyl group (–, enalaprilat) occupies the S1 pocket and the adjacent carboxylic 25
-
br Methods br Results br
2024-03-08
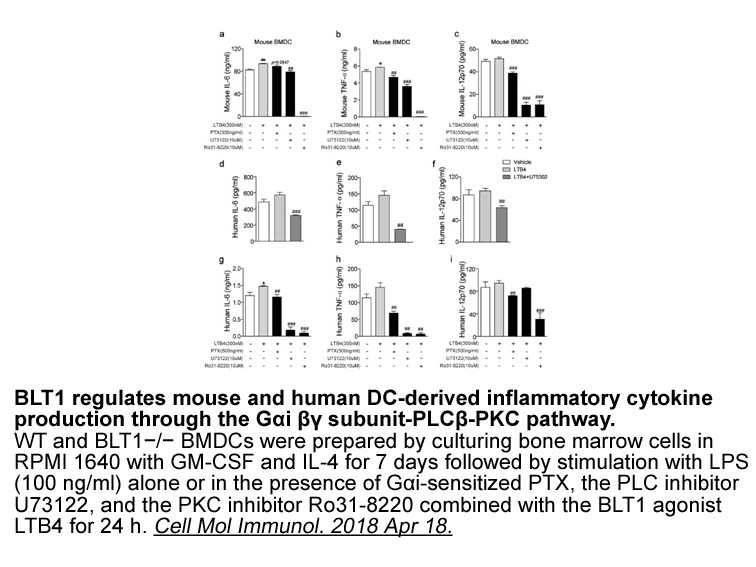
Methods Results Discussion Autotaxin has been shown to have effects on major cell types implicated in OA, notably chondrocytes, osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and synoviocytes, through its enzymatic product LPA [20]. However, a paucity of research exists on the involvement of autotaxin in OA. Fi
-
br The role of LOX plays in autophagy Autophagy
2024-03-08
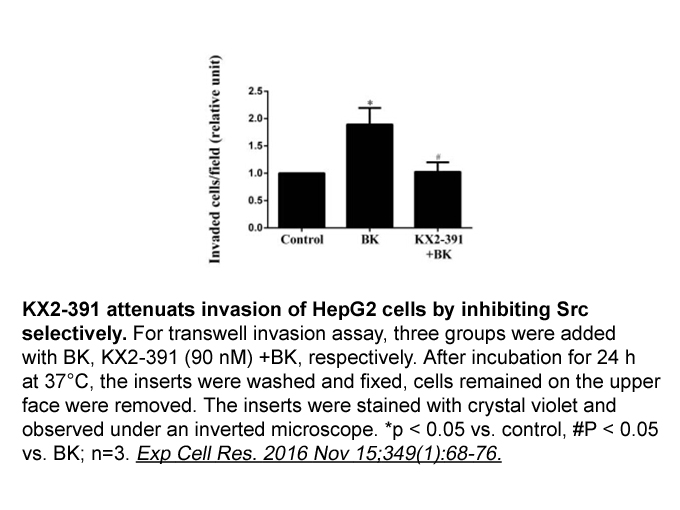
The role of 12/15-LOX plays in autophagy Autophagy is a process by which cellular material is delivered to lysosomal to degrade the damaged organelles and proteins to facilitate nutrient recycling (Towers and Thorburn, 2016). There has been characterized three types of autophagy-macroautophagy, m
-
Songbirds are outstanding models in the study
2024-03-08
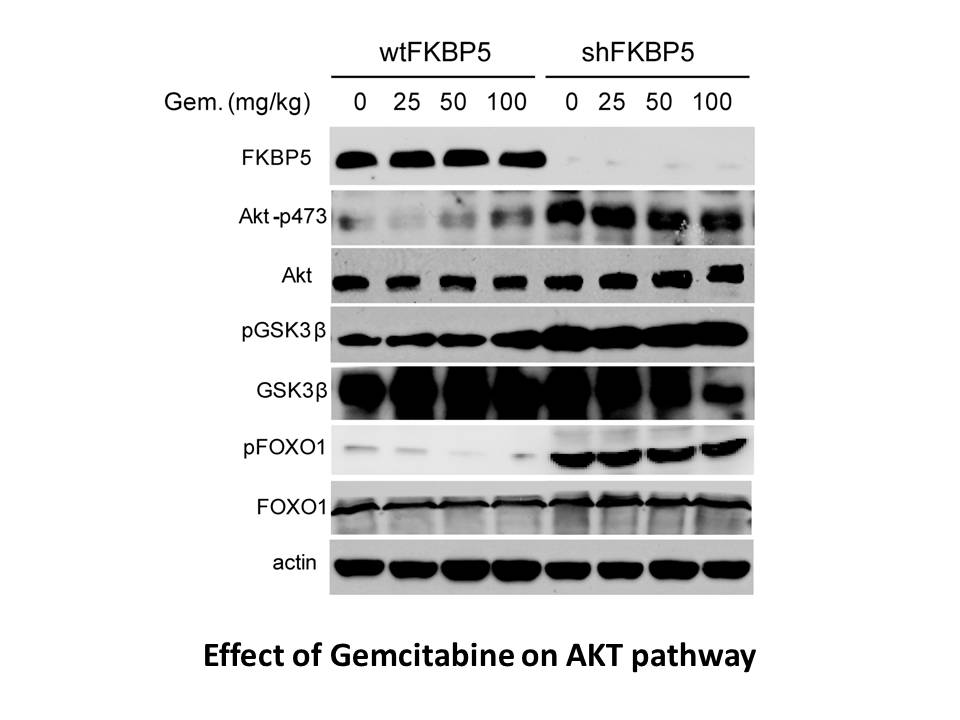
Songbirds are outstanding models in the study of vocal communication (Maney and Pinaud, 2011). Following the pioneering studies of William H. Thorpe and Peter Marler on the development of song in chaffinches (Fringilla coelebs) and white-crowned sparrows (Zonotrichia leucophrys) (Marler, 2004; Thorp
-
In previous years evidence emerged that inferred secondary m
2024-03-08
In previous years, evidence emerged that inferred secondary metabolites in plants might exhibit a potential arginase inhibition [36]. In a recent study, Pham and co-workers showed the inhibitory activity of chlorogenic Epothilone D (7) and piceatannol (8) (Fig. 3b) on mammalian arginase with IC50s o
-
Citral or dimethyl octadien al is a mixture
2024-03-08
Citral or 3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadien-1-al is a mixture of two stereoisomeric monoterpene aldehydes (the trans isomer geranial, citral A (40–62%)) and the cis isomer neral, citral B (25–38%) and serves one of the main constituent of essential oils of C. citratusis used in cosmetic, food, fungicides, p
-
The basis for the protonation
2024-03-07
The basis for the protonation of chitosan is the alkaline primary amino group, which is also the reason for the special properties of chitosan (Guibal, Van Vooren, Dempsey, & Roussy, 2006; Tamer et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2014). Our previous work (Meng et al., 2012) and several other reports (Yan et
16179 records 192/1079 page Previous Next First page 上5页 191192193194195 下5页 Last page